If you buy through affiliate links, we may earn commissions, which help support our product reviews.
Last Updated: Sep 22, 2023
The US has 31 active GPS satellites in orbit above the earth. GPS-equipped gadgets have become an essential part of our lives –from cars to smartphones.
Today, it has become impossible to get lost, no matter how hard you try. Walking with a smartphone in your pocket, you will have access to a GPS receiver with your exact position, no matter where you are.
Besides helping people reach their destination safely, there are other uses as well.
This article explores everything you need to know about GPS and even how GPS tracking works in car.
GPS Definition and How GPS Works
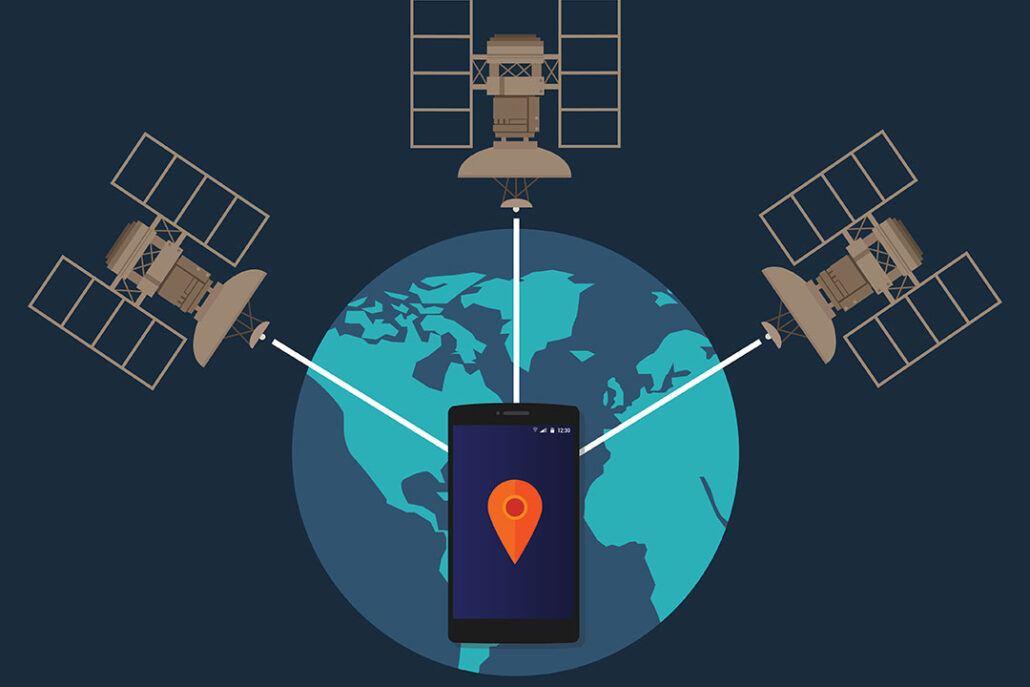
GPS, aka Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based system consisting of a minimum of 24 satellites. These satellites orbit Earth at an altitude of about 12,500 miles (20,000 km).
It works 24*7 across the globe regardless of the weather conditions. There are also no set-up charges or subscription fees to use it.
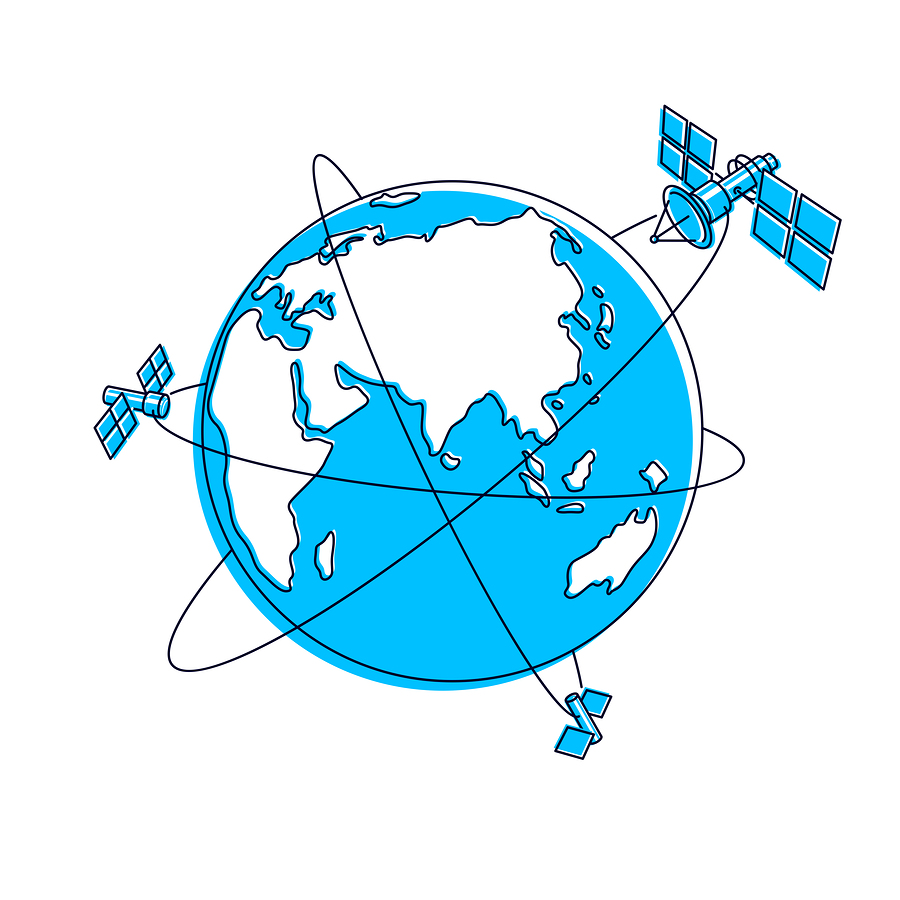

Components of GPS
GPS is a three-part system that includes:
a) Satellites – They serve like stars in the constellation.
b) Ground stations – They monitor and control satellites. Ground stations also identify their location.
c) Receivers – Receivers are constantly listening for signals from the satellites. Highly advanced receivers can even identify the exact location within a fraction of an inch.
Interesting GPS Facts
1. The original idea of the Geo Positioning System was based on LORAN and Decca Navigation System. Both were used during World War II to help in ship and plane navigation for long-range uses.
2. The 31 GPS satellites are US-owned. Each GPS satellite orbits earth (a full revolution) every 12 hours.
3. GLONASS is the Soviet version and consists of 24 satellites. They are in a faster orbit at 11,900 miles above earth and orbit in 11 hours.
Did you know you can actually see satellites orbiting the earth at night if you are in a dark area with no city lights around. Lay flat on your back and look up, give your eyes time to adjust.
They will look like tiny stars moving fast through the sky.
3. Doppler Effect is the fundamental principle used in GPS. Changes in signal frequency from the GPS satellites help in determining locations and speed.
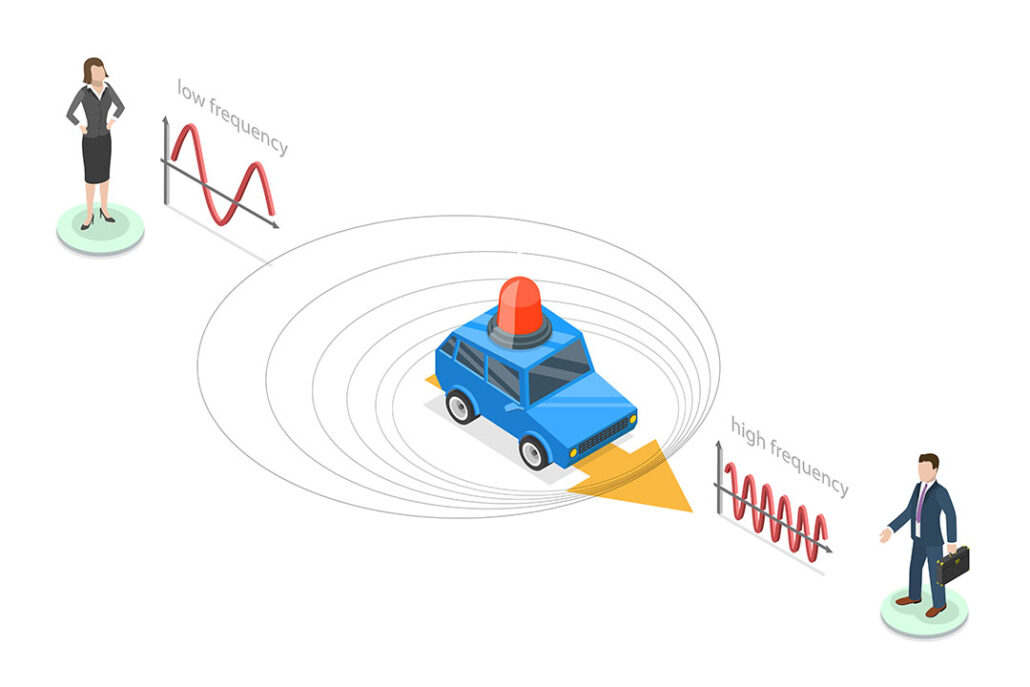
The Doppler Effect is critical to GPS functionality and many other systems in our world today, so it bears explaining.
All things are transmitted at a certain speed, i.e. light, sound, etc. So, if someone was running toward you and they threw a ball at you, the speed of the ball coming at you is their speed + the ball speed leaving their hands. If they are running away from you and threw a ball at you, the speed of the ball = ball speed – their speed.
This is the foundation of Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity, as he proved this with the speed of light.
4. Before GPS arrived, the navy navigation system was in use. Their requirement of a speedy navigation system forced them to think about whether the navigation system using satellites is possible.
5. In 1983, the Soviet Union shot down Korean Airlines flight as the flight moved through Soviet airspace. This incident made Ronald Reagan give public access to GPS for free.
6. When the Soviet Union launched Sputnik in 1957, two American physicists started monitoring the signal transmission of the satellite. They realized that they could determine the satellite in its orbit via the Doppler effect.
7. Early on, GPS was named Navstar. The first Navstar satellite was launched in 1978. The first completely built satellite was unveiled in the year 1989.
8. GPS was introduced in automobiles in 1996.
9. If you thought GPS is only associated with navigation, you were wrong. You can also use it to identify the correct time.
Each satellite possesses time signals and atomic clocks that GPS can use to transmit the right time. This time is critical to the GPS functionality and gives the ground receiving device the ability to calculate its distance and location.
10. Bradford Parkinson, Ivan A., and Roger L. Easton invented a GPS navigation system.

11. A man invented shoes known as ‘No Place Like Home.’ They have a built-in GPS that guides the person to home by clicking heels together three times.
12. The current worldwide market for GPS technology and is approximately over $2 billion. It is expected to increase over $30 billion in the next ten years.
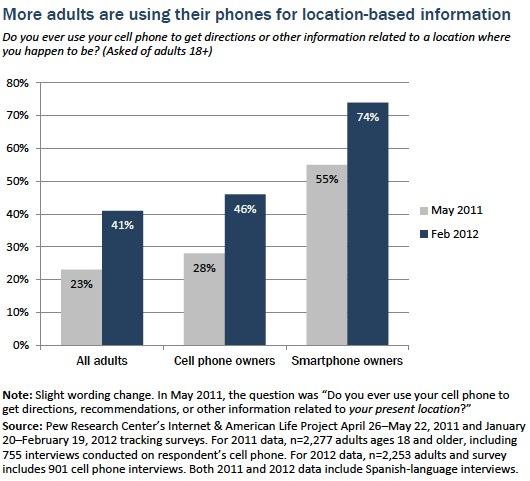
13. More than 74% of smartphone users use GPS to obtain real-time location.
14. You can use the phone’s GPS coordinates to share and track the location of other cell phones.
GPS History – How the Global Positioning System Came to Be?
- The Global Positioning System has its trace in the Sputnik era, where scientists use the navigation system to track the satellite with shifts in radio signal (Doppler Effect). This satellite was launched into orbit by the Soviet Union in October 1957.
- US Navy performed satellite navigation experiments in the mid-1960s to track US submarines.
- With 6 satellites orbiting the poles, submarines tracked satellite changes via Doppler and found the exact location of the submarine within a few minutes.
- The United States government initially innovated GPS for military use. Their need for a global navigation system arose during the cold war. Today the Global Positioning System is owned by the US Government and run by the US Air Force.
- In the early 1970s, the US Department of Defense wanted to create a strong and reliable satellite navigation system. So using past ideas from navy scientists, they decided to use satellites to support the proposed navigation system.
- DoD then launched its first navigation system, ‘NAVSTAR,’ in 1978. This system became completely operational in 1993.

At present, GPS offers two levels of service:
a) Standard Positioning Service
b) Precise Positioning Service
- PPS use is limited to United States federal companies, Armed Forces, and governments. SPS is available to any person for use without any charge with GPS receiver. There are more GPS receivers for civilians than military use.
- However, early civilian GPS systems were bulky and big. But they were not that accurate.
- To prevent intruders from using the navigation details, the US government used dithering. These global positioning systems were made available to common people for use in the year 2000s.
GPS Satellite Functionality
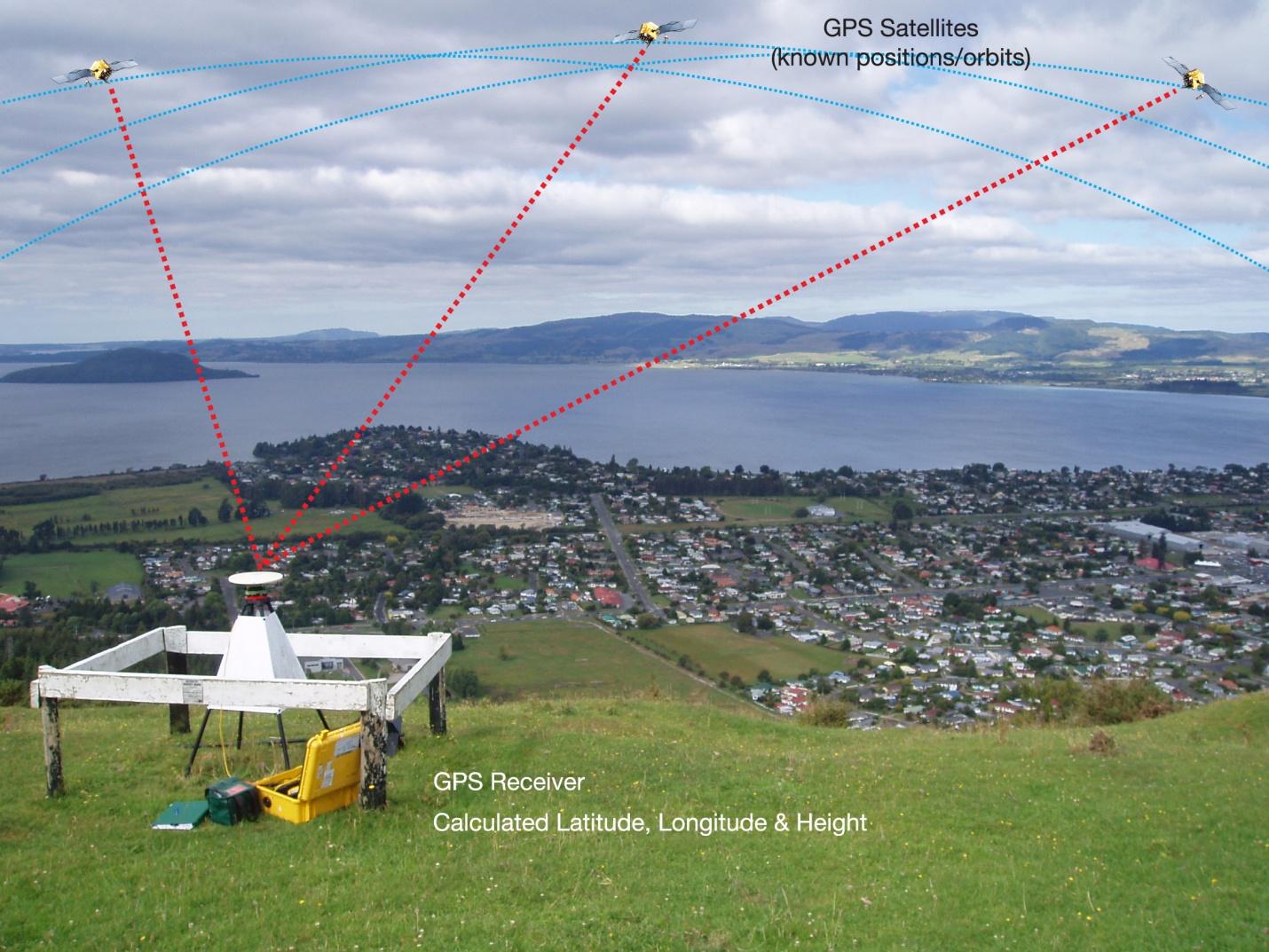
Each GPS satellite sends a unique signal to allow a GPS receiver to decode and calculate the exact location of the satellite. The signals move at the speed of light, the GPS receiver knows this, and this helps in the mathematical calculation to determine its position.

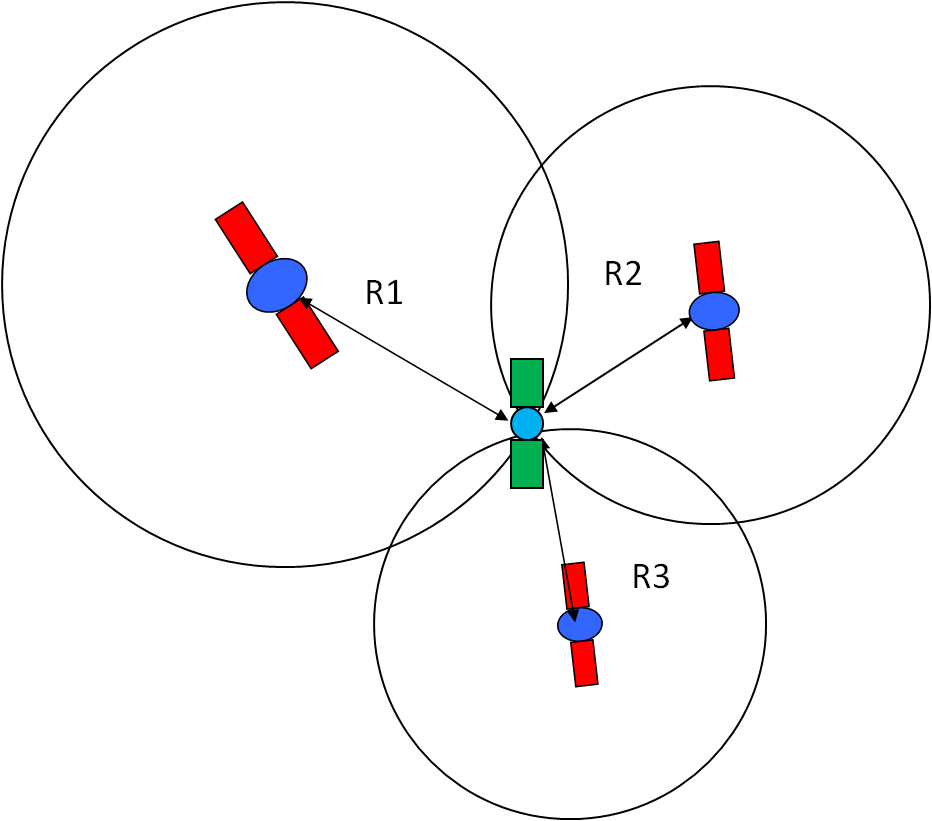
The GPS receiver uses this data to calculate the location of the user and show it on the electronic device using a process known as ‘Trilateration.’ It works by measuring the distance to each satellite by the total time it takes to receive a transmitted signal.
To compute the 2D position and track movement, the GPS receiver unit must lock on to the radio signal of a minimum of three satellites. Remember, four or more satellites allow the receiver to identify a 3D position fix.
Typically, a GPS receiver can track eight or more GPS satellites, but this depends on your location on Earth and the time of the day.
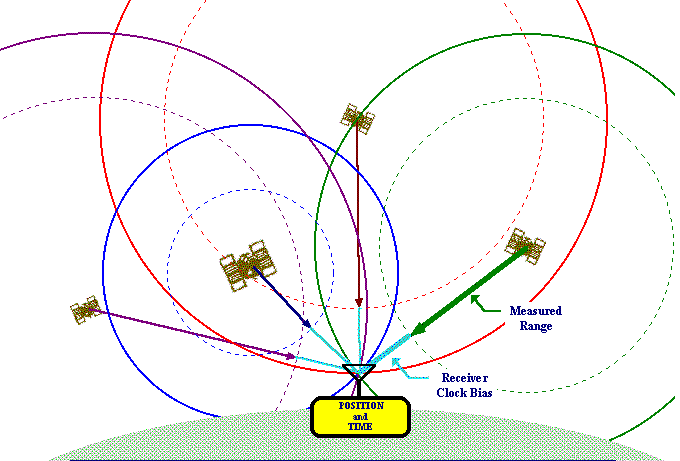
To complete the mathematical calculation; the GPS receiver uses the correct position of at least four satellites. The distance to each satellite estimates four crucial values:
- Earth latitude
- Earth longitude
- Elevation
- Time
Once a GPS receiver identifies the user position, it can calculate other metrics based on your next position and subtracting time and distance, such as:
- Trip distance
- Speed
- Bearing
- Distance to destination
- Track
- Sunrise, and sunset time
- Etc.
GPS Transmitted Signals
GPS satellites transmit at least two low-power radio signals. These signals are packed with three types of data:
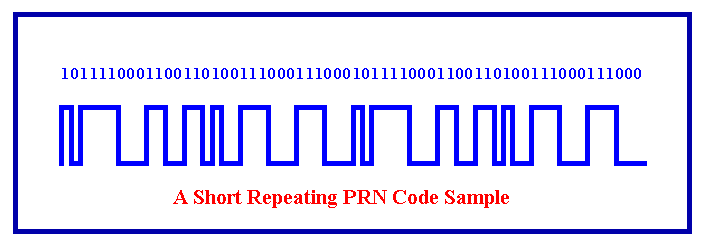
a) Pseudorandom Code
Each satellite has a unique pseudorandom code that identifies which satellite is transmitting data. It is a complicated code that contains a sequence of 1s and 0s.
The signal is so complex that it appears like random electrical noise. That is why, sometimes, it is known as pseudo-random.
b) Ephemeris Data
GPS satellites transmit details about the current time, location, and health through ephemeris data. Then use this data to estimate position relative to other satellites.
c) Almanac Data
GPS almanac data is the data that GPS satellite transmits throughout the day. It includes details like data in every satellite and state of the whole GPS satellite constellation. This data helps the receiver device locate an area of eligible satellites and get a “fix” much quicker.
Some Uses of a GPS
GPS Technology offers a lot of advantages:
Identify Location
Locating the position of the person in real-time and getting instant notifications is one of the biggest uses of GPS. It is a perfect tool for adventure lovers.
This is because the Global Positioning System helps them arrive at their destination safely and on time by displaying the best route available. This makes this tracking device one of the safest systems on the market.
Support in Emergency
Did you know approximately 2,000 people get lost in the woods every year?
So whether you get stuck in an isolated region or have an accident, features such as real-time tracking, route history, geofence zones, and alerts allow you to call emergency numbers on your phone with a GPS. Another essential tool for emergencies is the personal locator beacon, which emits a specific frequency that satellites pick up, ensuring rapid response in dire situations.
Another point is that it works even if you forget to share your location details with the emergency crew.
Prevent Car Theft
GPS can serve as a great anti-theft device. By installing it in your vehicle, you can track and locate it in case of theft.
Surveying
Many companies use GPS in surveying and mapping projects to do their job accurately and save time. These projects include crops, soil types, highways, etc. The point of GPS application is that surveyors can position it at a single point and set a reference marker to get precise locations.
Moreover, the valuable information obtained from the app can be transferred quickly into the software, allowing for a detailed chart.
Locate Criminals
Did you know Caracas, Venezuela is on top when it comes to crime?
Law enforcement, investigators, and police officials also use a GPS to catch criminals. They do this by adding a small GPS device on the vehicle of the suspect to track the location. It also helps them collect other valuable details too.
Find Lost Pets Quickly
Are you an avid pet lover? If yes, add a small GPS tracking device to their body. If your pet is lost, you can use it to locate them quickly.
Keep an Eye on Seniors or Disabled People
Another big benefit of GPS technology is you can use it to keep an eye on the elderly or disabled loved ones. There is a small button on these devices that seniors can press to make emergency calls for immediate medical help. SOS alarm notifies you when your loved one pressed it.
Did you know 5% of people in America ages 65 to 75 have Alzheimer’s disease? It is also ranked as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States.
In fact, statisticians also predict that in the next thirty years, 13.8 million people may be facing Alzheimer’s if researchers are not able to prevent or find a cure.
So if you have a loved one in your home that needs special care, you can use a GPS Tracker for peace of mind.
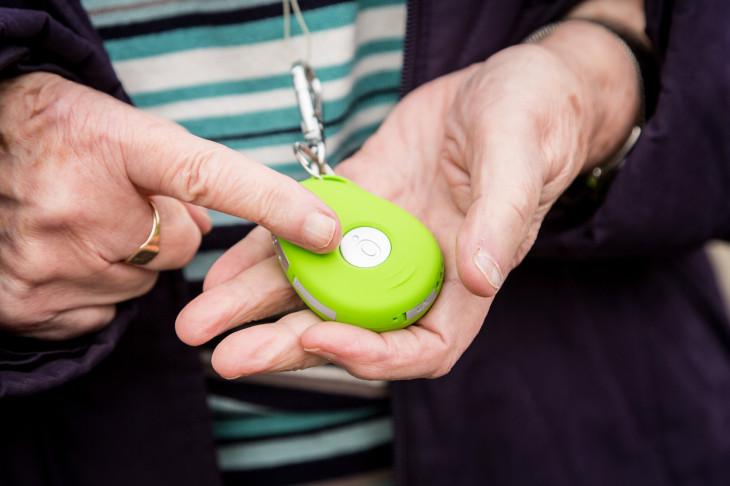

Today there are tons of GPS enabled devices you can add into the clothes or footwear of the elderly to track them or to track kids.
Protect Costly Artistic Pieces
Owners of valuable paintings and artwork protect their assets by installing a small GPS device in them. The moment it moves away from its location, it sends an email or text message to the owner to trace the location and get the artistic piece back.
Hunting Treasure
Technology geeks also use Global Positioning System to see treasure hidden on sites.
Disaster Management
GPS saves lives and ensures the speedy recovery of victims in case of global disaster. Location information coupled with automation effectively lowers delay in dispatch of emergency services and supplies. In fact, it operates in any kind of weather, anytime and anywhere.
Meteorologists use this modern technology for the prediction of storm and flood. They use GPS to assess water vapor content by analyzing data transmissions via the atmosphere.
Live Recording
Another benefit of GPS is real-time tracking and live streaming video recording.
Easy Linking to Tablet, PC or Mobile
You can even link your vehicle tracking system to your tablet, mobile, or PC to monitor location in real-time.

GPS Satellite Navigation
Satellite navigation (or Satnav) means the use of a portable radio receiver that picks up the signals from orbiting GPS satellites. It is usually more accurate than other forms of navigation.
The best example of this is Car GPS navigation systems.
Since it’s a broadcast system, so any number of people can use it. Navstar Global Positioning System is the popular Satnav system that uses 31 active satellites.
GPS Tracker
A GPS Tracker is a system used to track the precise position of any person or vehicle in a real-time scenario. It updates location using GPS Satellites, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
It must be in direct line of sight to at least three different satellites to triangulate the exact position. That is why most of the GPS trackers use Wi-Fi routers for the massively dense regions and indoor tracking.

However, to obtain a precise location from the Wi-Fi router, you require a Wi-Fi chipset in the tracker. These Wi-Fi routers work in the same way as satellites. However, it’s not as accurate as getting the location from satellites due to the fact that the router has an approximate address and not a precise location.
Learn more about how to use a GPS tracker.
How GPS Works in Car
Cars can contain many products that have GPS inside them. For example, Car Navigation and GPS Trackers will use the same GPS described above to get your location.
So, even if the car is moving fast, as long as these devices can receive GPS signals, they will work fine.
There are things that will prevent the GPS signals from being received in a car, like bad weather, and clouds can block GPS signals.
A poor install location, like, in the trunk, may block the signals, also.
There are 3 Types of GPS Tracking Devices:
a) Data Pushers
Data pushers are GPS tracking units that are used for tracking any vehicle, person, or asset. In asset and personal tracking, the location of a particular person or vehicle is sent to the server over short time intervals.
However, in-vehicle tracking, the GPS tracking unit doesn’t just send vehicle position to the server but also analyze the speed and other data needed.
b) Data Pullers
Data Pullers track location the same as data pushers. However, the main difference is that data pushers do not send any data to the server. Instead, it requests to send the information.
On the other hand, data pullers are always switched on and can be used to extract information at any time.
c) Data Loggers/Recorders
Data Loggers store the position of vehicle, speed, and heading in its internal memory. However, it does not send any data to the central server but can do so when retrieved by the user/owner.
How does a GPS Tracker Work
- A GPS Tracker works by getting the current location fix similar to the GPS receivers as described above.
- However, instead of displaying the current location on-screen on the equipment, it will transmit it to the server using the worldwide GSM cellular network or other radio signals.
- The server hosts a platform that end-users can access and see current location and speed, historical path, and other information.
- All the GPS data is transmitted using the web and shown on the device of end-user using a smartphone app, or desktop application.
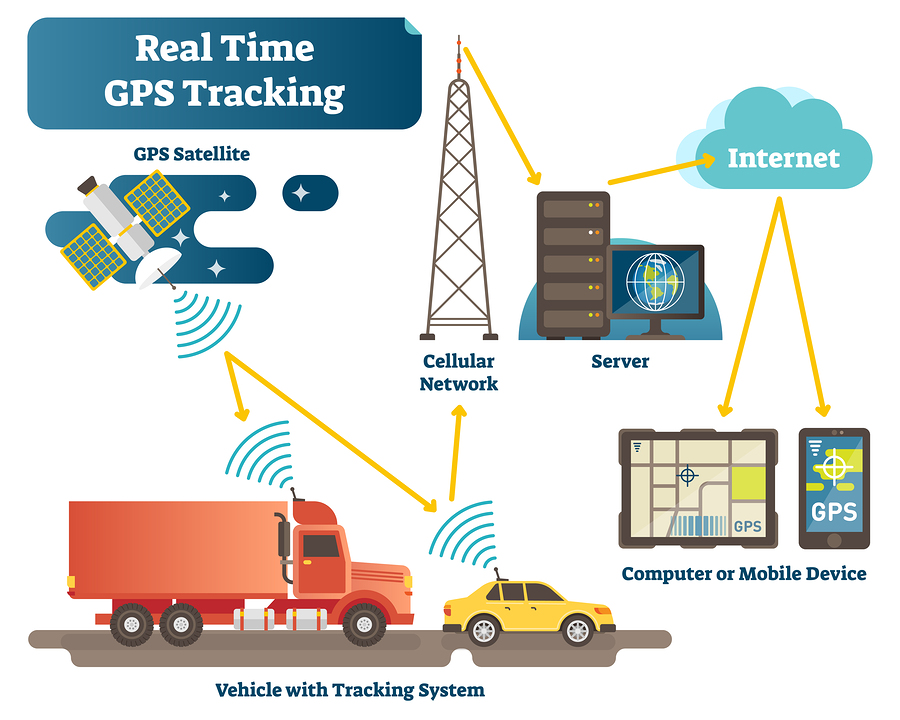
- In case GPS satellite signals are blocked, the GPS tracker can look for cell tower signals to estimate the location. The tracker estimates the location by calculating the distance between cell phone towers and adjacent towers using triangulation.
See our article about testing GPS trackers and a cell phone in a metal tool box.
Types of GPS Receivers
GPS Personal Trackers
Personal trackers track people or even pets. They work via their own devices such as a bracelet or pocket chip. They are pocket-sized and can be added to the pet collar or backpack of a person who is hiking for easy tracking and navigation. But you need to activate them to locate and follow the device remotely.
GPS Asset Trackers
GPS trackers are used to track many kinds of assets like boxes, crates, equipment, trucks, and even ATVs and 4x4s. GPS Tracking can be used in conjunction with RFID chips and satellite tags.
GPS Vehicle Trackers
As mentioned in the previous section, How GPS Works in Car, GPS is perfectly suited for use in a car.
Most GPS Trackers use cell-based racking. Cell-based trackers are most common.
Did you know cell phones make excellent trackers?
They collect data from where the vehicle is traveling and send it over the internet using cell towers.
See our article on Choosing a GPS Tracker.
Remoter users can access tracking information using a secure web connection or smartphone application.
- Plug-In GPS Trackers
Plug-in GPS trackers are easy to install into the port of a car. The port offers power and information to GPS trackers. They alert the owner if the vehicle is turned on or off. They are ideal for both business and personal use.
- Hardwired GPS Trackers
Hardwired GPS Trackers have a wire that fits into the vehicle. They offer more flexibility than a plug-in model. Since they are not attached to the port, they can be installed anywhere under the dashboard or other parts of the vehicle.
- Battery Powered Trackers
Battery Powered GPS Trackers are independent of the power system of the vehicle. They have long battery life and broadcast to monitors. They report to the network after sensing motion or at specified intervals.

Fitness & GPS Watch Trackers
Fitness GPS trackers are ideal for those who want to live an active and healthy lifestyle. These wristwatch-like trackers measure calories burned, number of steps, pacing, and distance covered. Solar GPS watches can track your location, monitor your heart rate and more.
Marine GPS navigation systems are very advanced systems that use GPS to navigate using chart plotters and fish finders. They feature a marine database and identity buoys and sound signals used in the navigation of the boat or vessel.
How to Choose GPS Tracker (Passive or Active)?
When picking GPS trackers, consumers decide if they need a passive or active tracker.
Passive trackers do not allow users to follow every motion of an object or person, no real-time tracking. They record or log the GPS data quietly.
Then, users gather and upload the data into a computer. These trackers are usually cost-effective as they do not have any monthly charges.
Active trackers process and offer information in real-time using a cellular transceiver or SIM. Dispatchers get the data via GSM cellular network. If consumers choose these services, they usually pay monthly fees.
To learn more about choosing a GPS Tracker, see our article here.
How Accurate is GPS?
GPS receivers available today are very accurate. Thanks to the parallel multi-channel design. When switched on, they quickly lock onto satellites and they maintain a tracking lock even in urban settings or regions with highly dense trees.
Factors that can Affect GPS Accuracy
Here are some of the factors that can directly affect GPS signal accuracy:
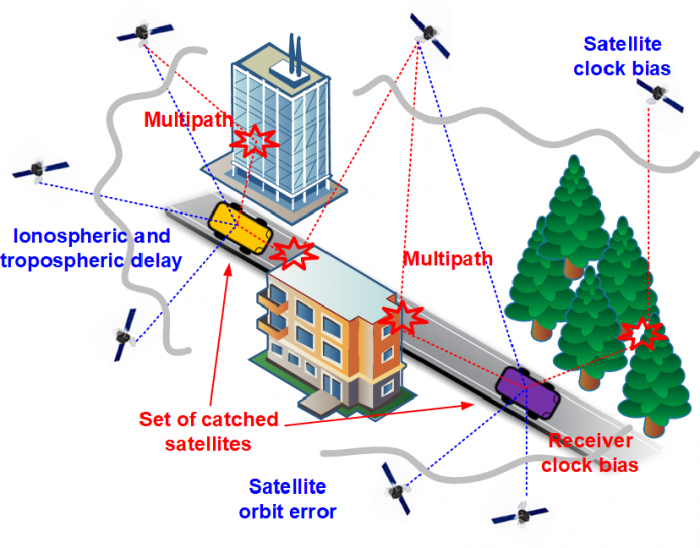
a) Quality of the GPS Receiver
Remember, the receiver with the clock is not as accurate as an atomic clock in the satellite. Atomic clocks are needed to calculate the exact time it takes to receive the GPS data.
b) Position of the Satellites
Satellite positions at the time the data is recorded can also affect GPS accuracy. For example, poor satellite geometry occurs when they are in tight groups or a line. Satellite signals are correct when located at wide angles to each other.
c) The Characteristics of Surroundings
Multi-path effects happen when radio signals get bounced around when coming in contact with buildings, valleys, tree cover, etc. The increase in the travel time causes room for errors.
Tips:
- Use a narrow collector method to identify the long delay of signals.
- There are also specially-built antennas that you can use to measure accurate data signals that get slightly deviated or delayed.
- Try modern high-sensitivity GPS receivers to track signals when under tree-cover or inside buildings.
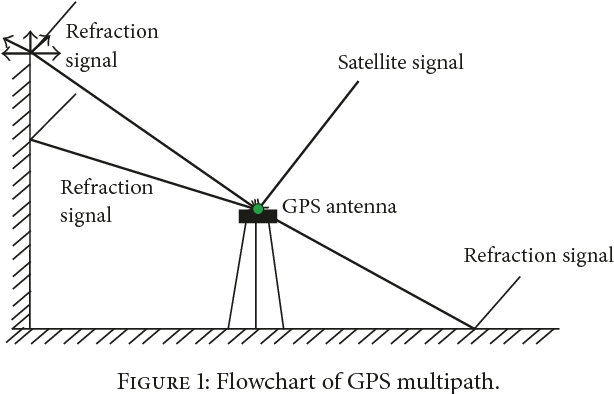
d) Weather Conditions
Any change in the atmosphere can affect GPS radio signals. Both the ionosphere and troposphere can leave a minimum or massive impact on the speed of radio signals.
Tips: Take into account dual-frequency measurement to lower flaws. It will also identify the precise location of the receiver.
e) Artificial Degradation of Signal
The US Department of Defense has restricted the public from using accurate GPS signals. Their main aim is to stop any misuse. Due to this, some intentional errors may occur, such as transmitting wrong orbital information, noise in the satellite clock, etc.
However the government turned off selective availability (SA) in May 2000 to enhance the accuracy of GPS receivers for civilian use.
f) Number of Satellites Visible
The more satellites a GPS receiver can spot, the better the accuracy. When the signal gets hindered, you may get position errors or no position at all. Remember, GPS units do not work underground or underwater.
Applications of GPS
As GPS technology improved, different industries have started adopting it. Here are additional applications:
Aviation
Did you know aircraft systems use GPS in hunting the best and safest route in the space? Yes, GPS allows the commanding station officials to track each route and movement on the plane in real-time.
This device also alters the pilots whenever there is a change in weather conditions or any other problem.
Grocery
Grocery retailer uses GPS technology to track the movement of consumers inside supermarkets. It helps them keep an eye on the shopping habits of visitors. They do this by adding a small device to their shopping cart.
Mining
Miners also use it to track certain minerals under the surface of the earth.
Farming
Farmers weed, plant, and harvest in a specific season. They simply add the GPS receiver to their tractors and other farm equipment. It helps them to identify which regions of land are perfect for fertilization and map their plantations as per that.
Farmers usually use this technology in foggy and winter seasons since GPS allows them to guide well.
The best agricultural GPS guidance systems are the latest advancements in agricultural technology, allowing farmers to map out their fields and efficiently manage their crops accurately. These systems provide precise navigation, detailed crop scouting information, and easy-to-use operation. They are invaluable for any farmer looking to maximize yields and improve overall efficiency.
Healthcare
Many pharmacies and health care systems hide a small GPS tracking device to track illegal activities, robbers, and burglars.
Fleet and Trailer Tracking
Many fleets and logistics companies, construction equipment, courier services, and other businesses use GPS for tracking in real-time.
GPS allows them to track the best route, therefore allowing them to cut down on cost and fuel. It helps them increase the overall efficiency of their business.

Science
Earlier scientists use plastic and metal bands to tag animals. It would help them to follow these animals and monitor their activity. However, the innovation of the Global Positioning System has helped scientists just to add the device to the animal with collars.
It automatically traces them in different locations and tracks their activity. Furthermore, earth scientists also use a GPS app to study how landscapes change with time.
Military
US Department of Defense was the first one to innovate the GPS. Since then, it has been used by other military forces around the globe.
Army officials today use it to map the location of vehicles and missiles during the war. It helps them protect their soldiers and manage resources conveniently.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications, mainly mobile telephone, use the application to offer reliability, accuracy, and stability in their work.
Wrapping Up:
The GPS and its systems are one of the most significant inventions of the 21st century and will continue to be with us for along time.
GPS FAQs:
How to Make a GPS Tracker
To make a GPS Tracker you will need 2 basic radio components:
A GPS Receiver, to get the current location.
A Cellular Transceiver or other Radio to transmit that data to the Cloud or Internet Servers.
You would also need a rechargeable battery or other connection to provide power to the GPS Tracker.
How GPS Works in Mobile Phones
Nearly all mobile phones are equipped with GPS receivers and cellular radios, including WiFi and Bluetooth. This allows them to find your location easily.
How GPS Works in Car
GPS works the same in a Car as in other vehicles. As long as the GPS signals can be received from the satellites above.